What is Content Delivery Network? (CDN)
As a website owner, you should be mindful of the performance of your website. This is where a Content Delivery Network can be helpful. It can make your website more accessible to people who come from all around the world. Before that, you should have a clear idea of what is content delivery network all about. From this article, we will help you to learn about the definition of CDN and what to expect.
What is CDN?
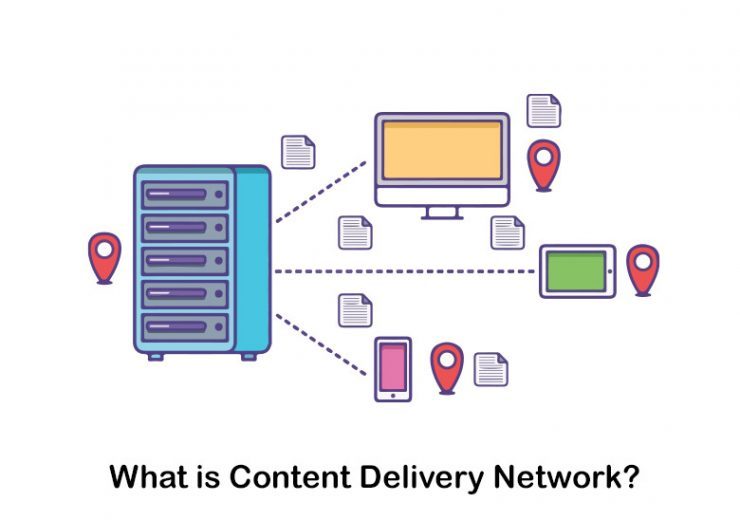
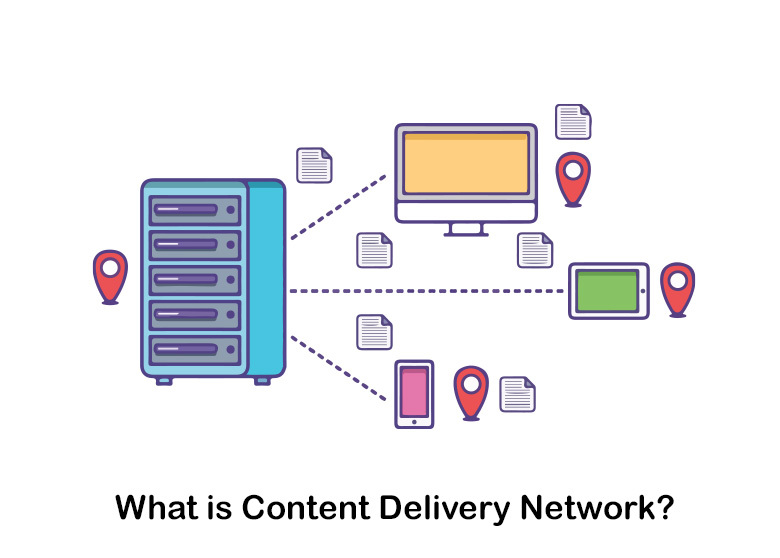
What is content delivery network? A content delivery network, also known as CDN, is a collection of geographically spread computers that speeds up online content delivery by bringing it closer to consumers.
Caching, a practice that temporarily saves copies of information in data centers across the world, allows you to access online material via an internet device or browser more swiftly thru a server located near you. CDNs cache web pages, pictures, and videos on proxy servers near your physical location. This eliminates the need to wait for information to load before watching a movie, downloading software, checking your bank balance, posting on social media, or making transactions.
A CDN may be compared to an ATM. Having an ATM on almost every corner makes getting money quick and easy. There are no lengthy bank lines, and ATMs are located in various accessible places for quick access.
CDN services were established to alleviate network congestion caused by sending rich online content such as graphics and video across the internet, similar to a traffic jam. It took much too long to get material from centrally situated servers to individual users. Text, graphics, scripts, and media files are now part of CDNs, software download speeds, e-commerce, portals, documents, social media sites, and on-demand or live media streaming sites. CDNs may also help defend websites from security threats and malicious attacks such as distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) assaults.
Benefits of CDN
Now you are aware of the definition of CDN. While keeping that in mind, let’s figure out the benefits you can get out of a CDN.

1- Improve website load times
Visitors see quicker page loading times by using a local CDN server to distribute material closer to website users (among other improvements). A CDN may minimize bounce rates and enhance the amount of time people spend on a site since visitors are more likely to click off from a slow-loading site. Alternatively, a speedier website will attract more people who will remain longer.
2- Reduce bandwidth costs
For website hosting, bandwidth usage charges are a significant price. CDNs may minimize the quantity of data an originating server needs to offer via caching and other improvements, lowering hosting expenses for site owners.
We have an article about what is bandwidth in web hosting that can help you out.3- Keep a website always online
Large quantities of demand or hardware breakdowns might cause a website’s usual operation. BECAUSE OF ITS DISPERSED NATURE, a CDN can better manage more traffic and resist equipment failure than multiple origin servers.
4- Protect data
A CDN may provide DDoS mitigation, upgrades to encryption keys, and other improvements to increase website security.
Why use CDN?
CDNs handle a significant amount of global internet traffic. They assist in overcoming the most challenging obstacles of providing material via the internet. Content delivery networks are used by businesses ranging from small & mid-content producers to the world’s largest organizations to give a consistent online experience to their consumers.

CDNs were created to help the internet run better since it was not meant to manage the demands of vast volumes of data, live elevated video, sale prices, and big downloads. They assist in the safe delivery of media at scale and allow all of the linked interactions that are now a part of most people’s everyday lives.
The difference between such a click that gives you instant access to fresh material and a click that gives you a seven-second delay as a load time or a video buffer is called performance. When an ISP’s internet access can’t supply data quickly enough, it causes buffering, which is represented by a recognizable whirling circle indicator on the screen.
Availability refers to the ability of a material to be accessed by end-users even when there is high user traffic, such as when many individuals are accessing it simultaneously or when there are server outages in certain regions of the internet.
As the number of high data and information on the internet grows, so does the number of attackers attempting to take advantage of it. Malicious actors may cost businesses a lot of money. DDoS and web-based assaults, along with crimes perpetrated by malevolent insiders, have been the costliest.
How does CDN work?
A CDN is a collection of servers connected to provide material as rapidly, inexpensively, consistently, and securely as feasible at its most basic level. A CDN will install servers at the intersections of several networks to boost speed and connection.

All the internet exchange points are the primary places where various Internet providers link to offer traffic originating on their respective networks to each other. A CDN provider can cut costs and travel time in elevated data transmission by connecting to these high-speed or highly linked sites. A CDN optimizes regular client/server data transfers and the positioning of servers in IXPs. CDNs establish Data Centers in crucial places throughout the world, improve security, and are built to withstand a variety of faults and Internet congestion.
Examples of CDN platforms
When trying to get a CDN, you will encounter many different service providers.- Akamai
- Edgecast
- CloudFlare
- Amazon CloudFront
- and MaxCDN
Conclusion
If your website has a global audience, it is a must to have a CDN. Keep these facts in mind and make sure that you get hold of the best CDN platform available out there to consider.